This document describes Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), an application-layer control (signaling) protocol for creating, modifying, and terminating sessions with one or more participants. These sessions include Internet telephone calls, multimedia distribution, and multimedia conferences.
Tag Archives: reference
The TCP Datagram
push flag (1 bits)
The push flag tells the receiving end of the tcp connection to “push” all buffered data to the receiving application. It basically says “done for now”.
via The TCP Datagram.
This would be the PSH flag that I needed to look up and found this site which makes for a good reference.
Transparent web proxy – DD-WRT Wiki
Running a transparent proxy server on your network can be used for more advanced content filtering of web pages for environments such as a school or library (where in some locales, filtering is required by law) or as a way to protect children in the household.
This guide will help you enable a transparent proxy server on your network by having your WRT54G router forward all traffic to the proxy server automatically.
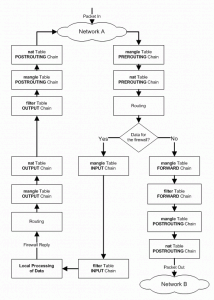
Linux Firewalls Using iptables
Quick HOWTO : Ch14 : Linux Firewalls Using iptables – Linux Home Networking.
This site was also linked here last May but is so useful I needed to bring it to the top again. Here’s a pertinent figure that describes the iptables process that I seem to need to reference all the time when editing the iptables config file.
20 Linux System Monitoring Tools Every SysAdmin Should Know
List of router or firewall distributions
This is a list of operating system distributions designed for use as the operating system of a machine acting as a router and/or firewall.
List of router or firewall distributions – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
XMPP Technologies Overview – The XMPP Standards Foundation
XMPP is the Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol, a set of open technologies for instant messaging, presence, multi-party chat, voice and video calls, collaboration, lightweight middleware, content syndication, and generalized routing of XML data.
XMPP was originally developed in the Jabber open-source community to provide an open, secure, spam-free, decentralized alternative to the closed instant messaging services at that time. XMPP offers several key advantages over such services:
via XMPP Technologies Overview – The XMPP Standards Foundation.
Force iptables to log messages to a different log file
Iptables is used to set up, maintain, and inspect the tables of IP packet filter rules in the Linux kernel. Several different tables may be defined. Each table contains a number of built-in chains and may also contain user defined chains.
By default, Iptables log message to a /var/log/messages file. However you can change this location. I will show you how to create a new logfile called /var/log/iptables.log. Changing or using a new file allows you to create better statistics and/or allows you to analyze the attacks
Protecting the pre-OS environment with UEFI
Quick summary
- UEFI allows firmware to implement a security policy
- Secure boot is a UEFI protocol not a Windows 8 feature
- UEFI secure boot is part of Windows 8 secured boot architecture
- Windows 8 utilizes secure boot to ensure that the pre-OS environment is secure
- Secure boot doesn’t “lock out” operating system loaders, but is a policy that allows firmware to validate authenticity of components
- OEMs have the ability to customize their firmware to meet the needs of their customers by customizing the level of certificate and policy management on their platform
- Microsoft does not mandate or control the settings on PC firmware that control or enable secured boot from any operating system other than Windows
Via Protecting the pre-OS environment with UEFI – Building Windows 8 – Site Home – MSDN Blogs.
Pd-extended and random-data streams
Here’s a little something I wrote to take the checksums from incoming data on a network and turn these into useful data in Pd-extended. We communicate the data via the OSC (OpenSoundControl) protocol.
This uses:
- tcpdump
- Some sort of fifo
- Perl (to build our OSC packets)
- Pd-extended